In the vast expanse of the ocean, an unassuming yet remarkable resource thrives – seaweed. While often overlooked, these aquatic plants are the source of a remarkable compound known as alginate. Extracted through a meticulous process, it has found its way into numerous industries, revolutionizing everything from food production to pharmaceutical formulations. This blog post delves into the fascinating world of alginate, tracing its journey from the depths of the sea to its diverse applications across various sectors.
The Origin
It is a naturally occurring polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed species, such as Laminaria and Macrocystis. These seaweeds, commonly referred to as kelp, are abundant in the cool waters of the world's oceans. The extraction process begins with the harvesting of these seaweeds, a practice that has been carried out for centuries in coastal regions worldwide.
The Extraction Process
The extraction of alginate from seaweed is a multi-step process that involves various chemical and physical treatments. First, the harvested seaweed is washed and dried to remove excess moisture and contaminants. The dried seaweed is then treated with an alkali solution, typically sodium carbonate, which helps to solubilize the alginate present in the seaweed.
The resulting solution, known as sodium alginate, is then filtered to remove impurities and unwanted residues. This is followed by the addition of a precipitating agent, such as calcium chloride, which causes it to precipitate out of the solution as insoluble calcium alginate.
The precipitated calcium alginate is then washed and processed further to remove any remaining impurities. Finally, the purified alginate is converted back into its soluble sodium form through a process called ion exchange, resulting in the final product – sodium alginate.
The Versatile Applications
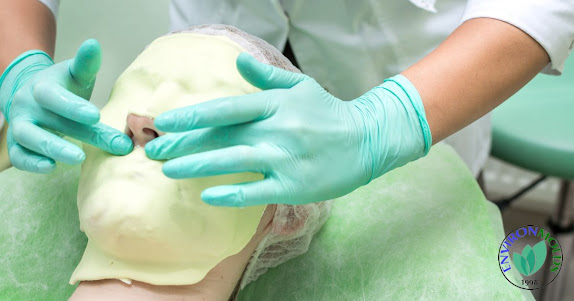
Due to its distinctive properties, this versatile compound is utilized across various industries in a myriad of applications. In the food industry, it is used as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier in products such as ice cream, salad dressings, and processed meats. Alginate is also widely employed in the pharmaceutical and biomedical sectors, where it is used in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and tissue engineering applications.
The textile industry benefits from its ability to improve the dyeing process and enhance the performance of fibers. In the cosmetic industry, it is utilized in various formulations, including facial masks, creams, and hair care products, due to its moisturizing and film-forming properties.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
As the world becomes increasingly conscious of the need for sustainable practices, the production and utilization of alginate offers several environmental advantages. Seaweed is a renewable and abundant resource, making it a more sustainable alternative to synthetic materials derived from non-renewable sources.
Furthermore, the extraction process of alginate is relatively eco-friendly, as it does not involve the use of harsh chemicals or generate significant amounts of waste. The byproducts of the extraction process can often be repurposed or recycled, further reducing the environmental impact.
Conclusion:
At Artmolds, we understand the importance of sustainable and innovative solutions in the ever-evolving industrial landscape. The journey of alginate, from the depths of the ocean to its diverse applications, exemplifies the potential of nature to provide remarkable solutions. As we continue to explore and harness the power of natural resources like seaweed, we move closer to a more sustainable and resourceful future. Embrace the potential of alginate and unlock a world of possibilities with Artmolds – "Shaping the Future, naturally."


0 Response to "From Seaweed to Solution: How Alginate is Extracted and Processed"
Post a Comment